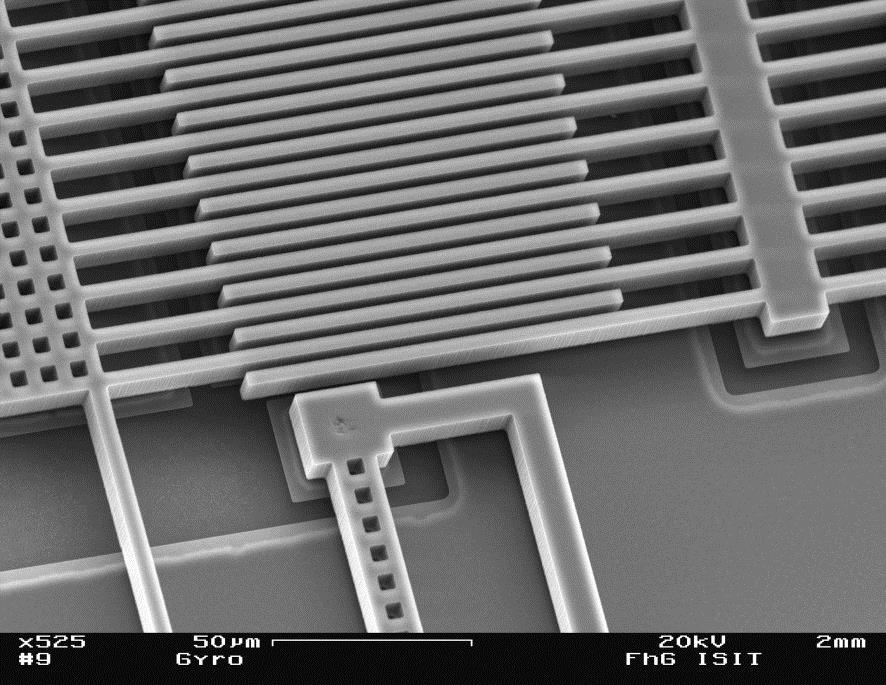
Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS) combine small device size with low cost in production and high reliability. This results in an increased application in the automotive industry, where MEMS inertial sensors are used for active and passive safety systems as well as for vehicle body control, e.g. electronic stability program (ESP) and navigation systems, even in cheaper models. Also consumer applications like mobile phones, laptops or game consoles urge for compact and low-cost inertial sensors. To enhance functionality and reduce size and cost of the sensor modules the development roadmap leads from one axis sensors to multi axis sensors on one chip and further on to a complete inertial measurement unit (IMU) on one chip.
Meanwhile sensors for measurement of rotation rates, accelerations and magnetic fields can be found in a variety of applications used in everyday life. Thanks to these sensors the use of many electronic products is - mostly unnoticed - much more versatile, simple and intelligent.
Numerous new applications in the field of consumer electronics as well as medical and security technology are the reasons for increasing market demands made on intelligent sensor systems particularly related to costs, size, quality, and power consumption.
These modules are made of three sensors for the measurement of rotation rates, accelerations and magnetic fields, each with three detection directions, forming a 9D IMU. This facilitates high precision measurement of position and orientation by evaluation of the terrestrial magnetic field and valuation patterns.
While 3-dimensional acceleration, rotation rate and magnetic field sensors are already industrially manufactured by means of chip level integration, their combination on one chip is far more demanding particularly with regard to chip design and manufacturing technology due to different requirements made on the operating environment. In the field of inertial measurement technology ISIT has developed the technology platform PSM-X2. The combination of acceleration, rotation rate and magnetic field sensors at chip level allows a highly integrated, precise and cost-effective production of IMUs.
Characteristic of the PSM-X2 process
- Silicon surface micromechanics process with a thick epi-polysilicon layer (up to 30μm) used for the moving mass on the sensor wafer
- Mechanical protection of components by wafer level capping (cap wafer technology)
- Hermetic encapsulation with very low leakage rates due to eutectic metal bonding systems (AuSi, CuSn, AlGe)
- Integration of a structured getter film into the cap wafer
- Adjustable working pressure inside the sensor cavities (1 bar up to 10-2 mbar)
- chip related leakage rate test using the "Neon ultra-fine leak test"
- Implementation of different working pressures inside of two adjacent cavities on one chip in one process step (dual cavity approach)
Sensor |
Gyrometer |
Magnetometer |
Accelerometer |
Mode |
Vibrating Mass |
Vibrating Mass |
Static Mass |
| Cavity Pressure | 250 µbar |
250 µbar |
100 mbar |
- 100% Testabdeckung durch speziell entwickelte Endteststrategie
- Prozess qualifiziert für automobile Anwendungen (AEC Q100)
 Fraunhofer Institute for Silicon Technology
Fraunhofer Institute for Silicon Technology