Sven Grünzig & Thorsten Giese
The Electrical Driving of MEMS Loudspeakers
One of the key areas at Fraunhofer ISIT is the development of highly miniaturized MEMS loudspeakers for Augmented Reality, Hearables, wireless headphones and hearing aids, among others. Besides the development and production of the actual MEMS components, a central aspect is the realization of suitable control electronics. In the group "Acoustic Systems and Micro Actuators" a new development kit was developed for this purpose.
Due to the piezoelectric drive and the resulting electro-mechanical properties, MEMS loudspeakers have a different behavior than conventional electro-dynamic loudspeakers. These differences have to be compensated by special drive electronics in order to be able to use the full potential of the MEMS loudspeakers.
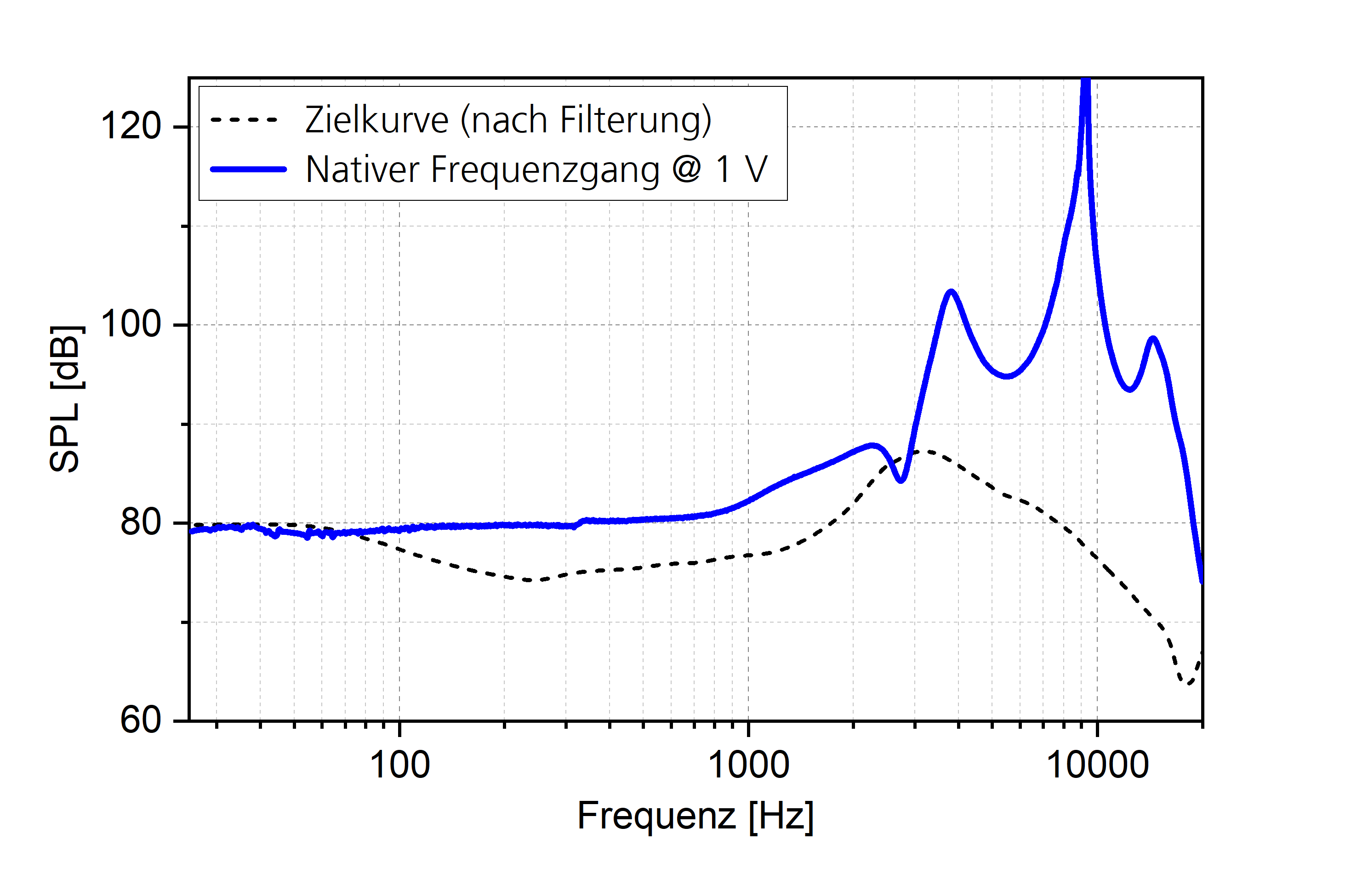
The sound characteristics of each loudspeaker are judged by the transfer function in the frequency domain, among other things. This transfer function reflects the sound pressure level (SPL) as a function of the respective frequency. Figure 1 illustrates this type of transfer function and shows the sound curve of a MEMS loudspeaker without acoustic adjustment of the music data (blue). Measurements were made with an IEC 60318-4 ear simulator from G.R.A.S., which simulates the human ear. Clearly visible is the mechanical resonance at 9 kHz, which leads to a significant increase of the acoustic amplitude and thus to distortions. To achieve the target curve (dashed line), a pre-filtering of the music data is performed, which is realized with the development kit.
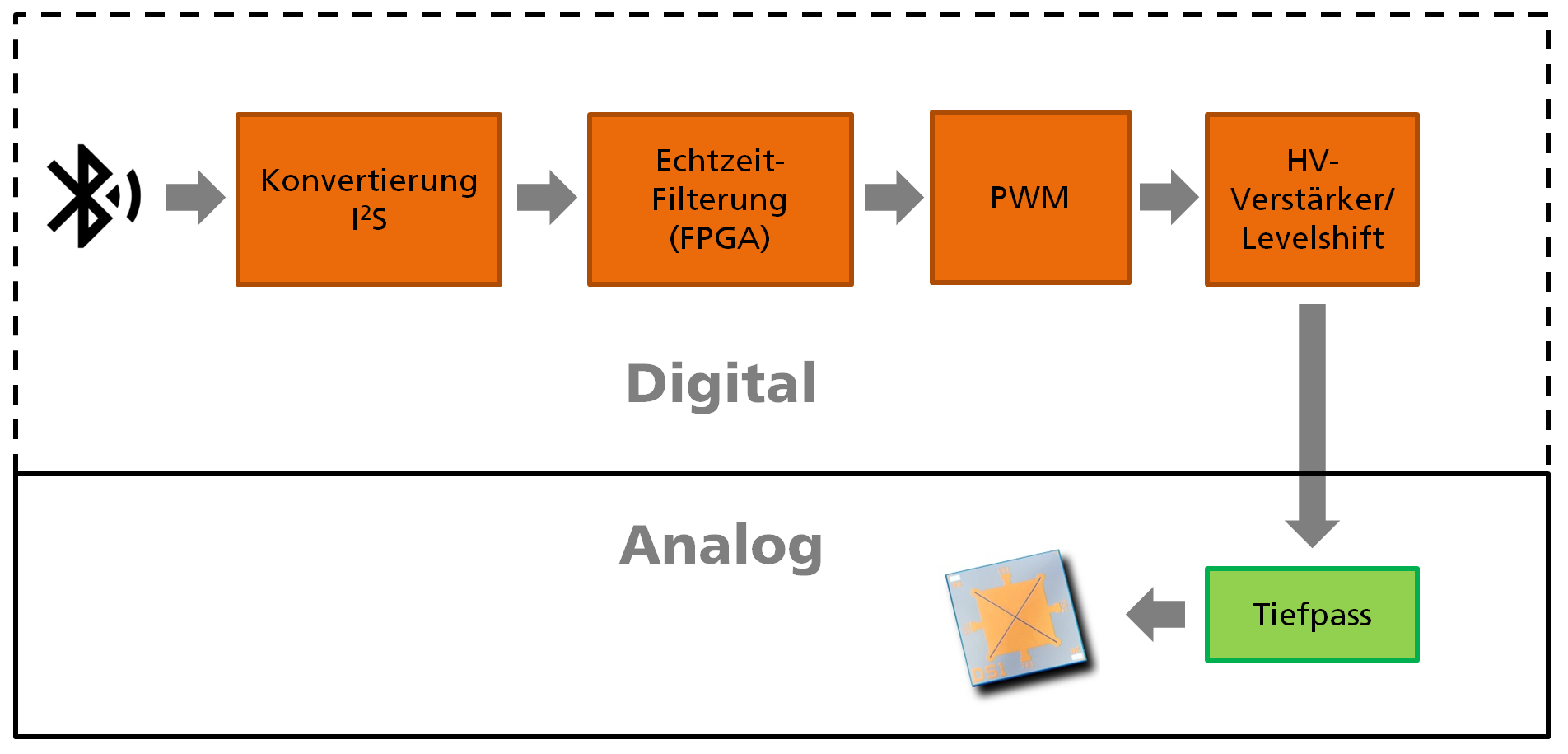
The task of this electronics is to receive the music data from a cell phone or other transmitter via a Bluetooth module and then convert it into the digital audio data format I2S (see figure 2). The data is only transferred from the digital to the analog domain directly before the MEMS speakers are controlled, which minimizes interference and noise to the audio signal. In addition, the Development Kit offers the possibility to drive not only MEMS loudspeakers with the previously used piezoelectric PZT layers, but also those with the new high-performance material AlScN, which requires a modified output stage.
The music data is pre-distorted in real time by FPGA-based hardware in such a way that acoustically e.g. the Harman sound curve or other sound curves are achieved. The MEMS loudspeakers are driven by particularly efficient digital pre-driver and power amplifiers and a final low-pass filtering to produce their powerful and clear sound. The realization of this development kit provides the group with a means for further characterization and optimization of various MEMS loudspeakers and forms the basis for highly integrated drive and driver electronics.
This might also be of interest to you
 Fraunhofer Institute for Silicon Technology
Fraunhofer Institute for Silicon Technology