Research & Development
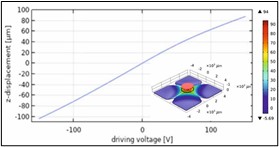
Besides our long term proven resonant mirror technology our new piezo actuator design and technology extends the application space substantially.
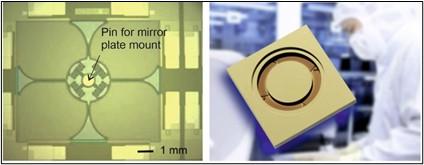
Fraunhofer ISIT's new generation of piezoelectric-driven MEMS scanners can achieve extreme optical scan angles close to 180° due to the high torque provided by the piezoelectric material. The achievable scanning speed and the ability to integrate two scanning axes in a very compact device are fundamental advantages of MEMS scanning mirrors over conventional galvanometric scanners.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Silicon Technology
Fraunhofer Institute for Silicon Technology